Page updated:
February 12, 2021
Author: Curtis Mobley
View PDF
Atmospheric Transmittances
[Howard Gordon also contributed to this page.]
Equations such as (3) of the Problem Formulation page and (13) of the Normalized Reflectances page involve various direct () and diffuse () atmospheric transmission terms, which require discussion.
Direct Transmittance
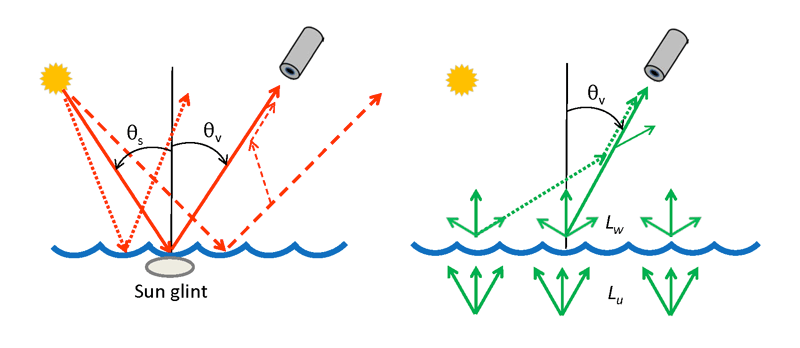
Direct atmospheric transmission is used if only one particular path, or a narrow bundle of nearly colinear paths, connects the source and the observer. This is the case for specular reflection, as illustrated in the left panel of Fig. 1. When the sea surface is viewed by the sensor, only a small patch of sea surface is seen as the Sun’s specular reflection or direct glint. Other points of the sea surface would be seen as localized patches of Sun glint for other viewing directions, but not by the sensor viewing direction as shown. In each case, the reflected radiance is traveling in a very narrow set of directions determined by the Sun’s location and the law of reflection ( for a level surface). The narrow beams of Sun glint for other viewing directions are represented by the dotted and dash lines in the left panel of the figure. These beams can influence the direction of interest only via two scatterings: the first out of the reflected beam and the second into the direction of interest. Such a two-scatter path is shown by the light dashed line. Two scatterings makes the contributions of the unseen beams of specular reflection to the direction of interest very small.
Let be the atmospheric optical depth along a vertical path (the nadir viewing direction for the sensor). This includes all effects of atmospheric absorption and attenuation by all atmospheric constituents. For an off-nadir viewing direction , the direct transmittance is then simply
| (1) |
This geometry is analogous to the Lambert-Beer law for radiance propagation of a beam through a homogeneous medium: , where is the beam attenuation coefficient and is the distance traveled. In the present case, , where is the distance though the atmosphere on a vertical (nadir-viewing) path, and is the atmospheric path length along the viewing direction.
Diffuse Transmittance
For water-leaving radiance , every point of the sea surface is emitting an upward distribution of radiance , as illustrated in the right panel of Fig. 1. Radiance from all locations and various directions can be scattered into the direction of interest via only one scattering, as illustrated by the dotted line in the right panel of Fig. 1. Radiance scattered out of the beam along the viewing direction can thus be replaced via a single scattering from the radiance emitted by a neighboring point propagating in a different direction. The diffuse transmittance therefore depends not just on the atmospheric properties and viewing direction, but also on the angular distribution of , which in general is unknown. This situation is analogous to the diffuse attenuation of downwelling irradiance within the water column of a plane parallel ocean that is illuminated at all points of the surface. Because radiance absorbed or scattered out of the path between the source and sensor can be replaced by radiance from other sea surface points and directions, the diffuse transmittance will be greater than the direct transmittance (just as the the diffuse transmittance is always greater than than the beam transmittance ). Accounting for the angular distribution of and for the scattering processes makes the computation of diffuse transmittance more complicated than for direct transmittance.
The diffuse transmittance of the water-leaving radiance along a particular viewing direction is by definition
| (2) |
where is the water-leaving radiance at the sea surface and is the water-leaving radiance that reaches the TOA. Henceforth, all quantities are assumed to be functions of wavelength, and the argument will be omitted. One way to compute is to run a coupled ocean-atmosphere radiative transfer model to compute the needed and for a wide range of atmospheric and oceanic conditions, Sun and viewing geometries, and wavelengths. The values of would then be obtained via Eq. (2) and tabulated for later use. Such tables would need to be constructed for all possible aerosol types (i.e, aerosol phase function shapes), aerosol optical thicknesses, water IOPs (or at least for chlorophyll concentrations in Case 1 waters), and viewing geometries. The tables would necessarily be large because of the large number of parameters that can affect .
Yang and Gordon (1997) examined the computation of diffuse transmittance and errors therein on the retrieved water-leaving radiance. Using a combination of radiative transfer numerical modeling of the ocean and atmosphere and reciprocity principles, they compared diffuse transmittances computed using realistic modeled and measured distributions versus diffuse transmittances computed on the assumption that is isotropic. Here denotes the upwelling underwater radiance distribution just beneath the sea surface. For a level sea surface, , where is the index of refraction of the water, the in-water is related to the in-air by Snel’s law , and is the Fresnel transmittance of the surface from water to air. When is isotropic, the diffuse transmittance is independent of the azimuthal angle and is denoted by .
Yang and Gordon (1997) (Eq. 3) show via a clever use of reciprocity that the diffuse transmittance of radiance along an atmospheric path in the direction of the Sun at solar zenith angle is numerically equal to the diffuse transmittance of irradiance from the TOA to a depth just beneath the sea surface, on the assumption that there is no upwelling radiance within the water. That is,
| (3) |
where is the downwelling plane irradiance just beneath the sea surface for an extraterrestrial solar irradiance incident onto the TOA at angle , and is the Fresnel downward transmission of the sea surface for radiance incident at angle from the normal. Since the upwelling radiance used to obtain this result is assumed to be isotropic, the azimuthal dependence of is irrevelant, and the desired diffuse attenuation for radiance at viewing direction is equal to the value of the irradiance transmission at the same polar angle. The great virtue of Eq. (3) is that it allows the efficient numerical computation of using backward (reverse) Monte Carlo simulation of downwelling irradiance for a given aerosol type and optical thickness.
The retrieved water-leaving radiance is, by Eq. (2),
| (4) |
Let denote the retrieval when rather than is used in Eq. (4). The error in the retrieved water-leaving radiance due to using rather than the exact is
| (5) |
Yang and Gordon (1997) found that for viewing angles perpendicular to the principle plane (the plane of the Sun), the errors in the retrieved are no more than 4% for viewing angles , Sun zenith angles , and aerosol optical thicknesses typical of clear atmospheres. The errors in band-ratio algorithms were less; e.g., the error in (used to retrieve chlorophyll concentration) is less than 2% except for very clear water and some viewing directions, for which the error in the ratio is about 3%. These parameter ranges covered most of the needs for SeaWiFS and errors of this magnitude were deemed acceptable compared to other errors in the retrieval process (i.e., removal of atmospheric path radiance). In that case, the diffuse attenuation can be obtained by pre-computed functions of the form
| (6) |
where and are tabulated for each aerosol type. Thus, for angles , only numbers and need to be tabulated for each aerosol type. Moreover, the aerosol type and optical thickness are determined as part of the process to remove the aerosol contribution to the total path radiance. This enables selection of the appropriate , and , and evaluation of Eq. (4) is operationally feasible. If aerosols are ignored, Eq. (6) reduces to , where is the Rayleigh optical thickness. This is the formula used in the early days for CZCS atmospheric correction. The value of Eq. (6) is that it allows the aerosol optical thickness to be incorporated into the diffuse transmittance calculations via a simple exponential and pre-computed and values.
However, for larger off-nadir viewing angles , for azimuthal viewing directions near or 180 deg, and for very clear water, the errors can be as much as 6%. This could be significant for the MODIS Aqua sensor, which views a wide range of directions. Gordon and Franz (2008) therefore re-examined the model of Yang and Gordon (1997) and developed a correction term to so that Eq. (4) becomes
| (7) |
The factor corrects for the bi-directional effects resulting from the use of an isotropic in the computation of , rather than the exact, non-isotropic . The needed for computation of was obtained from and chlorophyll-based models for and . Again, the correction term can be pre-computed and tabulated for various aerosol types and water IOPs. Evaluation of the impact of the correction applied to both SeaWiFS and MODIS Aqua data showed that retrieved water-leaving radiances will be in error by no more than if and the correction is omitted. For , i.e. near the edges of scan lines, the use of the correction is warranted.
In current operational practice, the tabulated and functions are applied for both downwelling (solar irradiance) and upwelling paths. The correction of Gordon and Franz (2008) is not applied because it is an added complication with no significant impact in most instances.

 See comments posted for this page and leave your own.
See comments posted for this page and leave your own.